Inflammation is your body’s natural response to harmful stimuli. When you suffer a cut, burn, or another type of physical injury, your immune system sends certain cells to that area to repair it and help it heal properly. These are known as inflammatory responses. Reducing inflammation in the body is important for overall health and disease prevention.
Inflammation is a hot topic these days. Many foods and products claim to reduce inflammation. But what is inflammation, and why are we trying to reduce it? In this article, we will define inflammation, note the difference between acute and chronic inflammation, and share tips for how you can reduce your inflammation. Understanding these concepts is key to making lasting lifestyle changes and supporting a healthier you.
Inflammation
Inflammation is an integral part of the body’s immune system. Our bodies need inflammation to stay healthy and prevent disease. Your body activates the inflammatory response when it encounters injury or infection. The inflammatory response defends the body against foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria, and helps to heal damaged tissue. This means that short periods of inflammation are part of a properly functioning immune system.
Acute Inflammation
Acute or short bouts of inflammation occur in localized areas and impact only the area needing. The cardinal signs of inflammation are heat, redness, pain, and swelling. Acute inflammation occurs in response to injuries like cuts or sprains and viruses, like a cold. When any tissue in the body is injured by bacteria, trauma, toxins, heat, or any other cause, the inflammatory response is initiated. Damaged cells release chemicals that cause blood vessels to dilate and leak fluid into the tissues. This causes swelling and delivers white blood cells to the injured area. White blood cells “eat” germs and damaged cells to clean up the area and reduce the chance of infection. This response is critical for the body to fend off damage and sickness. This is called chronic inflammation if the inflammatory process continues for a long period.
Chronic Inflammation
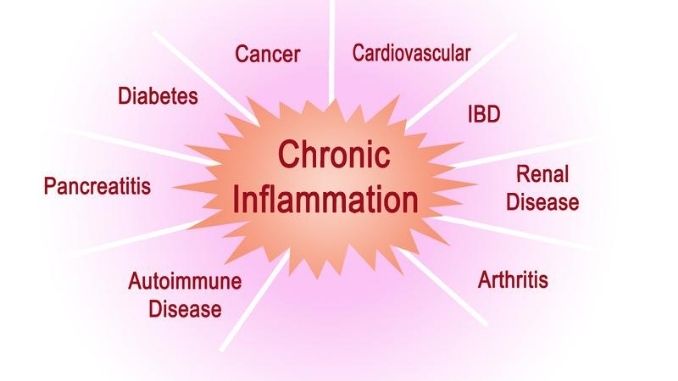
Long-term or chronic inflammation can cause damage to the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to the development of many diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. More research is needed to determine how chronic inflammation negatively impacts the body, but we know that long-term inflammation does not support health. Luckily, a healthy diet and exercise can help keep inflammation under control.
How to Reduce Inflammation
Now that we know the difference between acute and chronic inflammation, how do we prevent or control chronic, long-term inflammation? Always speak to your doctor before making any lifestyle changes.
1. Eat an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet is very similar to the Mediterranean diet. This includes fish, fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, and nuts. There is a limited amount of red meat, and red wine can be had in moderation. Anti-inflammatory foods contain components such as omega-3 fatty acids, which help protect the body against damage from inflammation. A rule of thumb is to eat more plants, as plants contain anti-inflammatory nutrients that your body needs to reduce inflammation. Plants include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Always make sure you are focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, as they pack the most nutrients and will not contain any harmful additives.
2. Focus on Antioxidants
Antioxidants are important as they help prevent, slow, or repair damage caused by inflammation. Antioxidant-rich foods include colorful fruits and vegetables such as berries, leafy greens, beets, and avocados. Beans, lentils, whole grains, ginger, turmeric, and green tea also have antioxidant qualities.
3. Eat Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are important for regulating your body’s inflammatory process. You can find omega-3 fatty acids in salmon, tuna, mackerel, walnuts, pecans, flax, and soy.
4. Eliminate Processed Foods
Try to cut out or reduce the consumption of processed foods. This includes products such as cereal, sugary drinks, deep-fried foods, and pastries. These foods are usually found in the middle aisles of the grocery store, while whole foods are generally located around the store’s perimeter.
5. Avoid Inflammation-Inducing Foods
Foods high in saturated and trans fats can increase inflammation. This includes red meat, dairy products, and processed and fried foods. Limiting or eliminating your sugar intake is also a good idea, which means consuming less refined carbohydrates (think white rice or white bread) and sweets. Cooking oils and margarine high in omega-6 fatty acids should also be avoided, such as corn, safflower, and sunflower oil.
6. Exercise
Studies have shown that regular exercise reduces systemic inflammation. Exercise also increases the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, chemical messengers that help regulate the inflammatory process. You only need 20 minutes of daily exercise to reap the anti-inflammatory benefits. In one study, participants walked on a treadmill for 20 minutes daily and saw anti-inflammatory effects.
7. Control Your Blood Sugar
Keeping your blood sugar healthy is essential for many health outcomes. This can often be accomplished through smart food choices. Limit simple carbohydrates, like white flour, white rice, white pasta, or products with high fructose corn syrup. These foods will spike your blood sugar and lead to diabetes over time. Structure your meals around lean proteins such as chicken, fish, or legumes and high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
8. Manage Stress
Chronic Stress can lead to inflammation. Learn to manage your stress through yoga, meditation, exercise, breathing practices, counseling, or anything else that works for you. Reducing your Stress will positively impact all areas of your life.
As you can see, there are a variety of ways that you can prevent and manage chronic inflammation. It is important to remember that there are simple things you can do every day to improve your health and well-being and that small steps over time can lead to some incredible results. Reducing inflammation will also contribute to your overall health and wellness by lowering your risk of chronic disease, increasing your energy and lots, and improving your daily feelings.
We have an EASY way for you to eat healthier… without giving up any of your favorite foods! Learn more here.