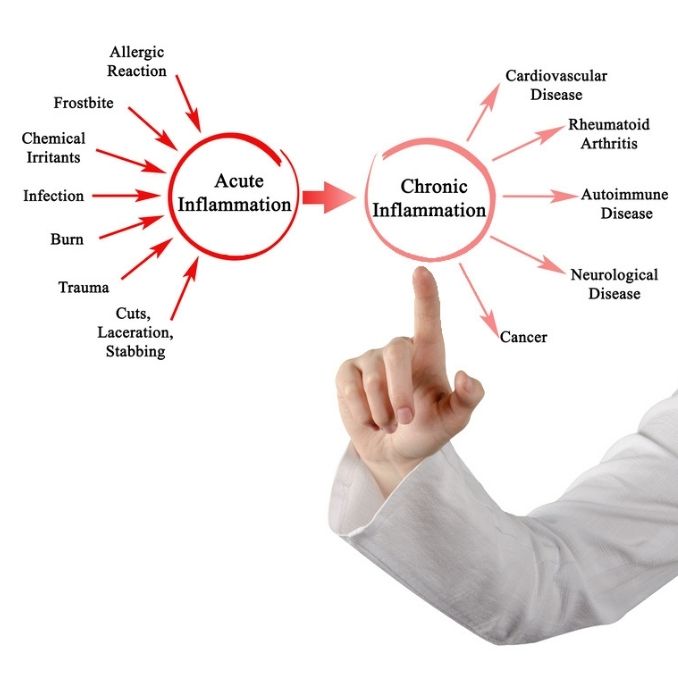
What comes to your mind when you hear the word inflammation? Is it joint and muscle pain after a workout, a sore throat from the flu, physical bruising, or redness and swelling after a bee sting? These are all examples of acute inflammation, inflammation specific to one area of the body. In this way, inflammation is not a bad thing. It is your body’s natural healing process. Inflammation only becomes detrimental when it becomes chronic.
You might be suffering from chronic inflammation if you have frequent infections and experience body pain, fatigue, insomnia, diarrhea, mood disorders, and several other symptoms. Chronic inflammation lasts for prolonged periods, usually several months to years. Often chronic inflammation symptoms are subtle, so they are easy to ignore or overlook.
Many health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and bowel disorders, have been linked to chronic inflammation, so managing inflammation to reduce your risk of long-term damage is essential. The extent and effects of chronic inflammation vary with the cause of the injury and your body’s ability to repair and overcome the damage.
Common Signs & Symptoms of Chronic Inflammation
- Low Energy & Fatigue: An imbalance of energy availability and expenditure can leave you tired, despite having a good night of sleep.
- Joint & Muscle Pain: It’s normal to feel sore after an intense workout or physical activity, but it is not normal if you are sore every day.
- Brain Fog: If your brain lacks the readiness to reach and maintain an alert state and you can’t figure out why inflammation is a likely culprit.
- Digestive Problems: This can be caused by an imbalance in gut bacteria, resulting in a bloated stomach, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Chronic Allergies: This is caused by persistent and repetitive exposure to allergens.
- Depression and Anxiety: The link between these two disorders and inflammation has been shown in studies.
Causes of Chronic Inflammation
The causes of chronic inflammation can vary, so it is essential to get to the root of the problem to decrease the damage being caused. Below we have shared some of the most common causes of chronic inflammation:
- Persistent Infections or Pathogens: Some organisms, such as fungi, protozoa, and parasites, are challenging to eradicate.
- Untreated Causes of Acute Inflammation: This includes infections and injuries.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Sometimes, your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues.
- Long-term Exposure to Toxins and Irritants includes industrial chemicals and polluted air.
How Does Chronic Inflammation Impact the Body?
When you have chronic inflammation, your body’s inflammatory response can eventually damage healthy cells, tissues, and organs. Over time, this can lead to DNA damage, tissue death, and internal scarring.
How Can You Keep Chronic Inflammation Under Control?
If you read health articles or watch videos about health and wellness, you’ll often hear the terms’ anti-inflammatory diet’ and ‘supplements’ linked with inflammation. This is because the foods that you consume can play a significant role in controlling chronic inflammation in your body. Below we have shared some of the best anti-inflammatory foods you should add to your diet and other helpful hints for decreasing inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
- Tomatoes
- Olive oil
- Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collards
- Nuts like almonds and walnuts
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines
- Fruits such as strawberries, blueberries, cherries, and oranges
- Fermented foods such as yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut
- Broccoli
- Avocados
- Green Tea
- Peppers
- Mushrooms
- Grapes
- Turmeric
While the foods above help to fight inflammation in your body, there are also specific foods that can worsen your condition. Do your best to reduce or eliminate the following foods from your diet:
- Refined sugar
- Margarine and vegetable oil
- Refined carbs
- Ultra-processed food
Best Anti-Inflammatory Supplements
- Curcumin
- Fish Oil
- Ginger
- Resveratrol
- Spirulina
Remember that it’s always important to check with your doctor when it comes to supplements. Follow dosage instructions carefully and purchase any accessories from a reputable manufacturer.
Sleep
Sleep is your body’s time to recover and repair your tissues. Make sure you get at least 8 hours of sleep daily. Studies have shown that not getting adequate sleep can trigger several different inflammatory responses in your body. There is no better reason to invest in getting the quantity and quality of sleep your body desperately needs.
Exercise
Recent research has linked exercise to reducing chronic inflammation. A combination of aerobic exercise with resistance training is recommended for the best anti-inflammatory impact, but 30 minutes of brisk walking is better than not moving.
Stress
Prolonged periods of stress can lead to increased levels of cortisol being released into the body. Over time, this decreases tissue sensitivity and impacts the effectiveness of cortisol in regulating inflammatory and immune responses. Inflammation becomes a stress response, so reduced stress means reduced inflammation.
If you don’t take care of your body, your immune system attacks over time, and it can destroy your tissues. If you are battling chronic inflammation, the best action is to make healthier lifestyle choices, including avoiding smoking and limiting your alcohol intake. Making a few simple lifestyle changes today can be the key to decreasing inflammation in your body and improving your overall health long-term.
Learn the best ways to eliminate inflammation through proper diet and nutrition. Click here for more information.