Thyroid disorders affect at least one in eight women and sometimes men. Due to the general nature of thyroid disorder symptoms, over half of those with a thyroid disorder are unaware of their condition. Recognizing the symptoms of a thyroid disorder early on can help expedite the diagnosis and treatment process. A poorly functioning thyroid can lead to various diseases and disorders, so identifying your condition early on is essential. Here is more information about recognizing thyroid disorder symptoms and what to do if you think you may have one.
The thyroid gland is your master gland. It is responsible for energy production and metabolism throughout your entire body. Due to its widespread functions, thyroid disorder symptoms are diverse and can affect different body parts. An underactive thyroid gland is referred to as hypothyroidism. This condition is most common in women during transitional times, such as during pregnancy, after childbirth, and during menopause. Men can develop hypothyroidism from chronic stress or environmental pollutants. An overactive thyroid gland is called hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism may not cause any noticeable symptoms in its early stages.
 Causes of Hypothyroidism:
Causes of Hypothyroidism:
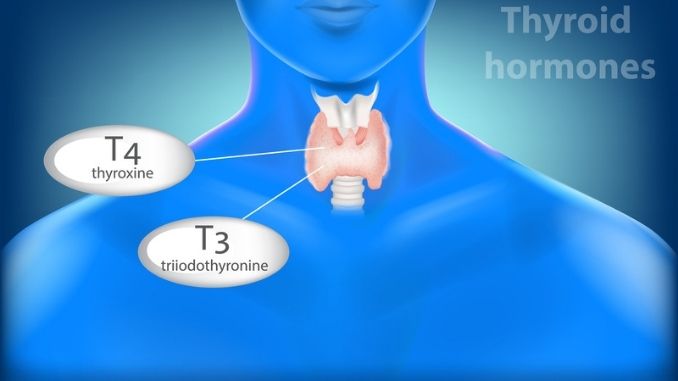
The hormones produced by the thyroid gland – triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) have a huge impact on your health. They influence all aspects of your metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. When the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, it upsets the intricate balance of hormones and chemicals in the body. Causes of hypothyroidism include the following:
- Autoimmune Disease: The most common cause of a hypothyroid disorder is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder. An autoimmune disorder is when your body’s immune system attacks your tissues, which can sometimes involve your thyroid gland.
- Hyperthyroidism Treatment: When too many thyroid hormones are produced, this is called hyperthyroidism. If there is an overcorrection, thyroid hormone production can be lowered, causing hypothyroidism. The treatment for hyperthyroidism often involves radioactive iodine or anti-thyroid medications.
- Radiation: Cancer treatments of the head and neck can impact the ability of the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones and may result in hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid Surgery: For those who have had all or a large portion of their thyroid removed, decreased, or stopped, thyroid hormone production will occur. In this case, thyroid hormone replacement will be necessary for the rest of their life.
- Medications: A variety of medications can contribute to hypothyroidism. If you are taking any medications, ask your doctor about the effects they might have on your thyroid.
The signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism are variable, depending on the severity of the hormone deficiency. Usually, problems develop slowly over several years.
Common Hypothyroid Symptoms:
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Unexplained Weight Gain
- Constipation
- Increased Sensitivity to the Cold
- Hair Loss/Brittle Hair
- Brain Fog
Common Hyperthyroid Symptoms:
- Anxiety/Irritability/Nervousness
- Having Trouble Sleeping
- Losing Weight
- Enlarged Thyroid Gland/Goiter
- Muscle Weakness/Tremors
- Irregular Menstrual Periods/Menstrual Cycle Stops
- Heat Sensitivity
- Vision Problems/Eye Irritation
Health Concerns that Could be Attributed to Your Thyroid:
- Anxiety/Panic Attacks
- Depression
- Generalized swelling
- Puffy Eyes/Face
- Muscle Aches/Pain
- Muscle Weakness
- Joint Pain/Stiffness/Swelling
- Low Sex Drive
- Asthma/Allergies
- Migraines
- Recurrent Miscarriage/Infertility
- Lack of Ovulation
- Decreased Memory
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- High Cholesterol
- Low Heart Rate
- Insomnia
- Hives
Hypothyroidism treatment is usually simple, safe, and effective. Usually, synthetic thyroid hormones are used as replacement therapy for hypothyroidism. Thankfully, accurate thyroid function tests can be used to diagnose thyroid disorders. If you are feeling tired for no reason, or have any other signs and symptoms discussed above, make sure to see your doctor.
 Causes of Hypothyroidism:
Causes of Hypothyroidism: